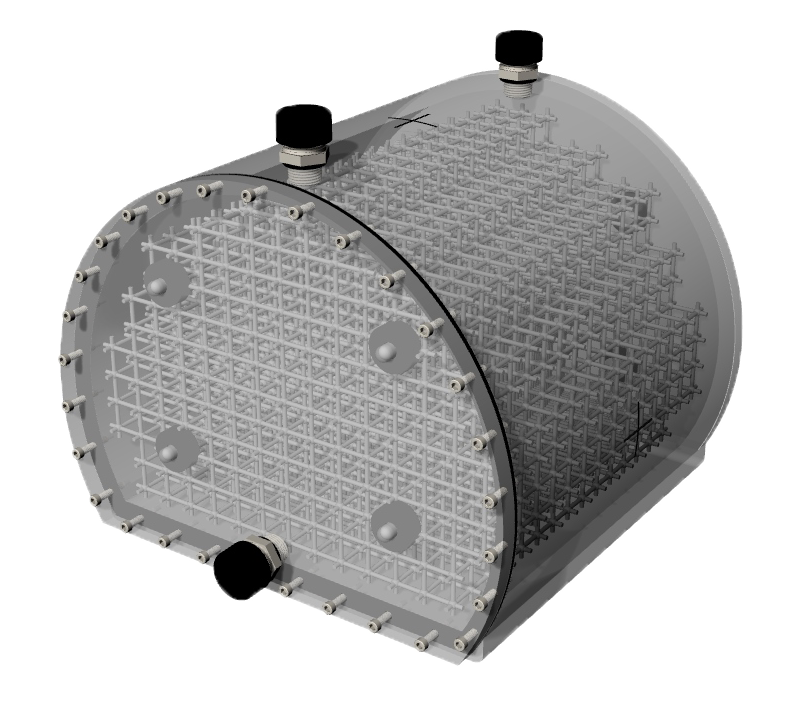
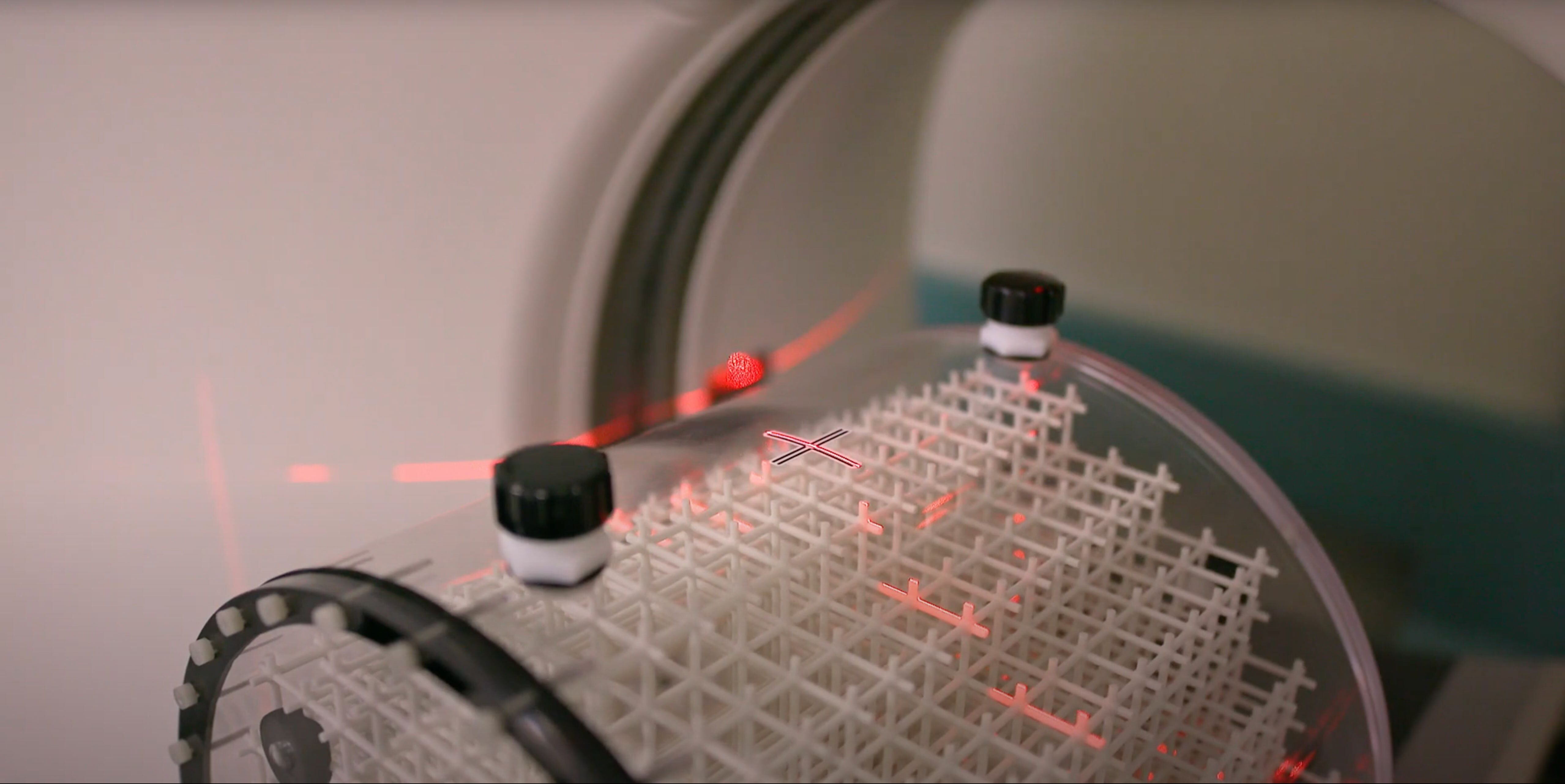
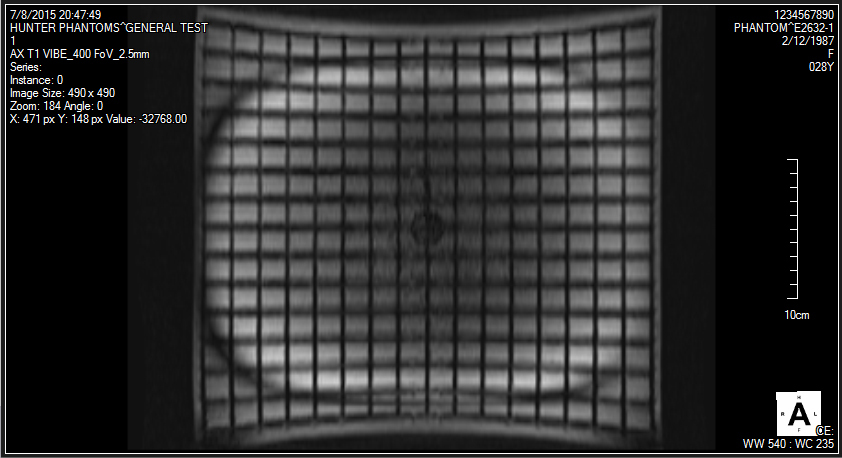
The Large Field MR Distortion Phantom provides a tissue-like imaging environment for assessing geometric distortion in whole-body MRI scanners.
Assess Image Distortion in a Tissue-Like Medium
The Large Field MR Distortion Phantom enables assessment of image distortion caused by B0 inhomogeneity and nonlinearity of the magnetic gradients.
Unlike air-filled phantoms, the Large Field MR Distortion Phantom is liquid-filled, making it sensitive to chemical shifts and susceptibility artifacts, which can be additional causes of distortion found when encountering density differences in diagnostic MRI and radiation therapy treatment planning.
Unique, Complete and Easy to Use
The phantom features a unique orthogonal 3D grid that provides complete geometric data throughout the imaging volume. Users can fill the phantom with the AAPM TG 100 recommended solution, or with specialized solutions for high-field MRI or unique scan sequences. Ground-truth measurements of grid locations can be obtained through CT scanning of the phantom.
The phantom is marked for ease of alignment to position lasers and is designed for use with both curved and flat gantry tables.
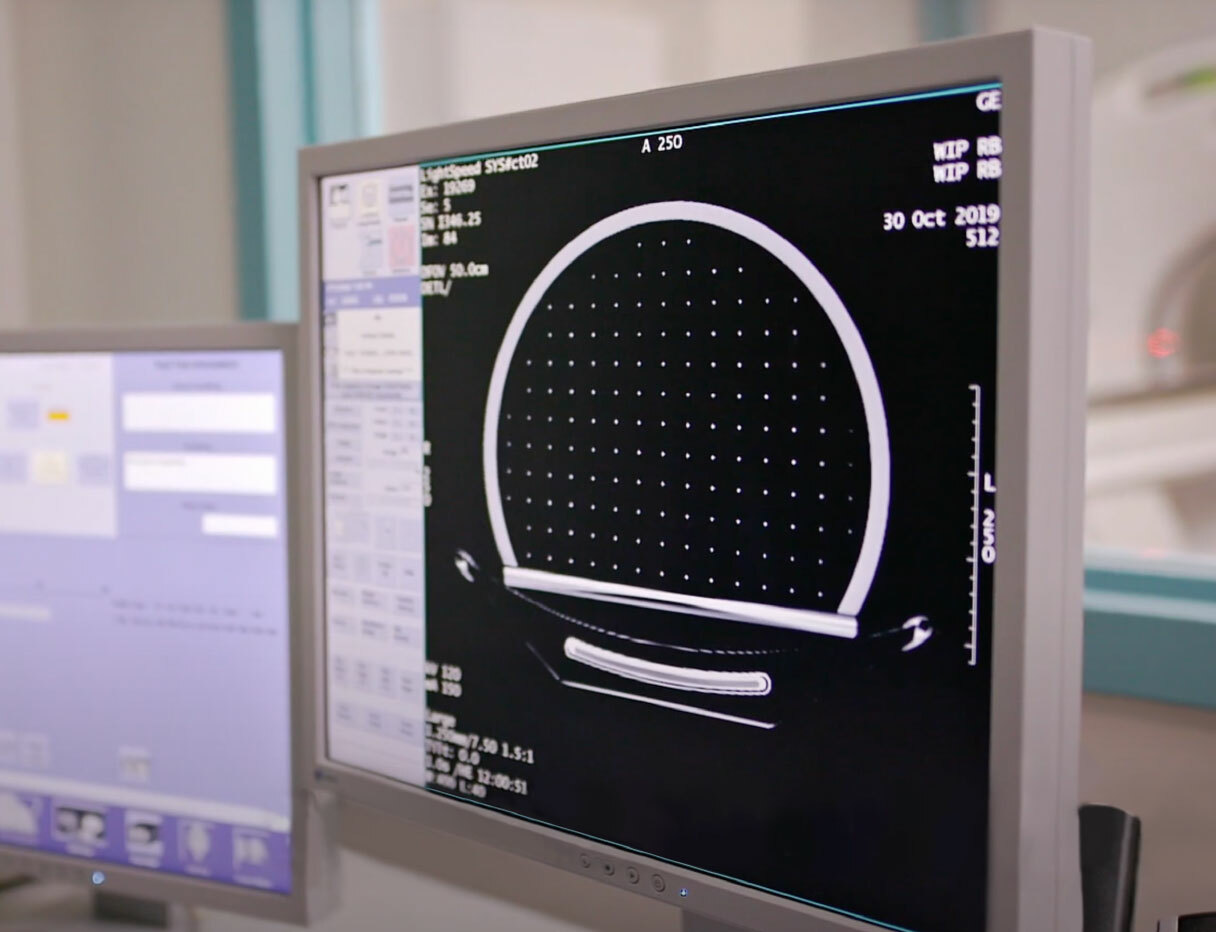
Automated Analysis of Distortion in MRgRT
Used with MRI Grid phantoms, Distortion Check software quickly and automatically quantifies distortion in MRI images. Simply scan the phantom, upload images, review reports and trend analysis, and export DICOM overlays.
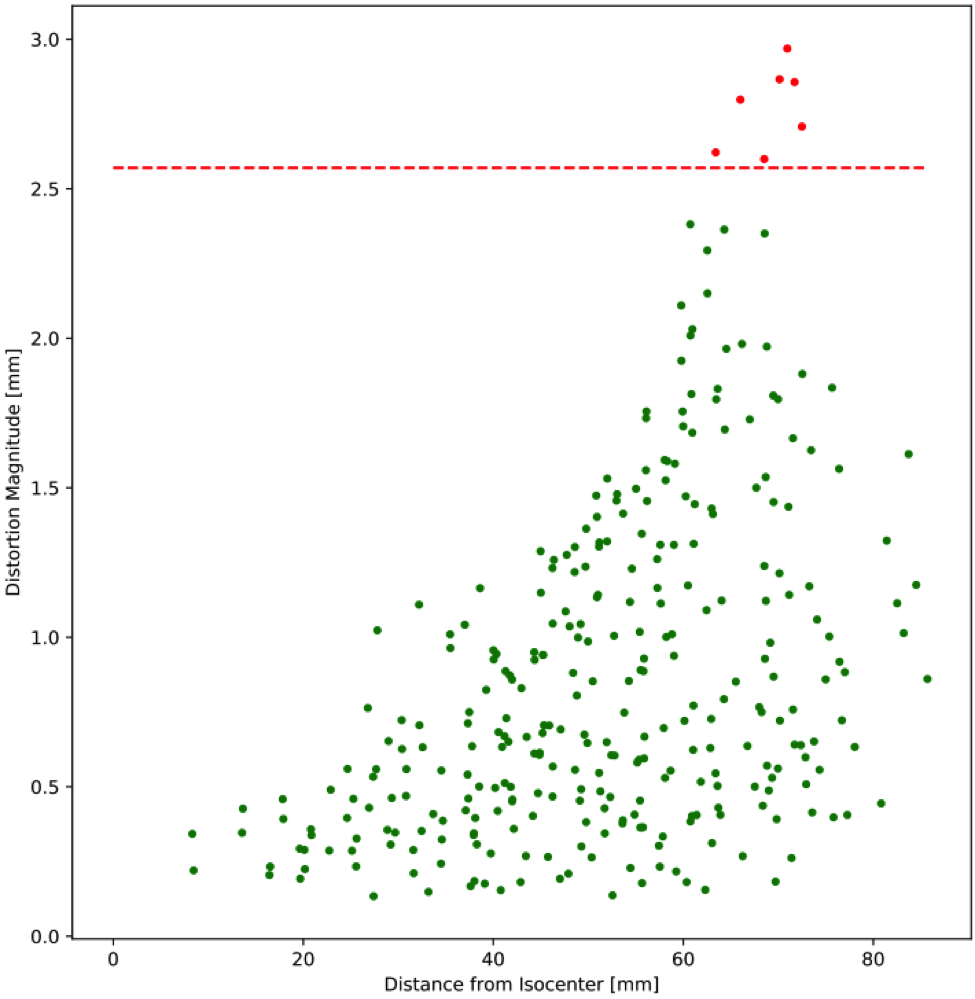
The software registers either a ground truth CAD or CT scan to the detected control points. An interpolation is then performed to generate the 3D distortion vector fields.
Results can be reported in a variety of output formats including scatter plots, contour plots, box and whisker plots for trending, and DICOM overlays that can be exported to third-party software
Software Features
- Quickly and automatically analyze complete MR data sets
- Density of control points optimized to bring interpolation close to linearity
- User-friendly cloud-based solution
- Detailed format in NEMA MS 12 standard recommendations
- Easily analyze and track multiple machines, imaging sequences and phantoms
- Establish distortion tolerance thresholds specific to different imaging sequences
Start building your MR Distortion program.
The Large Field MR Distortion Phantom has been successfully tested in multiple sequences including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, 3D Time-of-Flight, MPRAGE and CISS.
Resources
Specifications
Material |
PMMA |
Weight (Dry) |
17 lbs (7.7 kg) |
Weight (Filled) |
62 lbs (28.1 kg) |
Dimensions - L/H/DIA (cm) |
30 x 27.6 x 30 |
Grid Spacing |
20.3 mm (I-S), 20.5 mm (AP) and 21.5 mm (L-R). Grid intersections enhanced by 6 mm diameter sphere. |