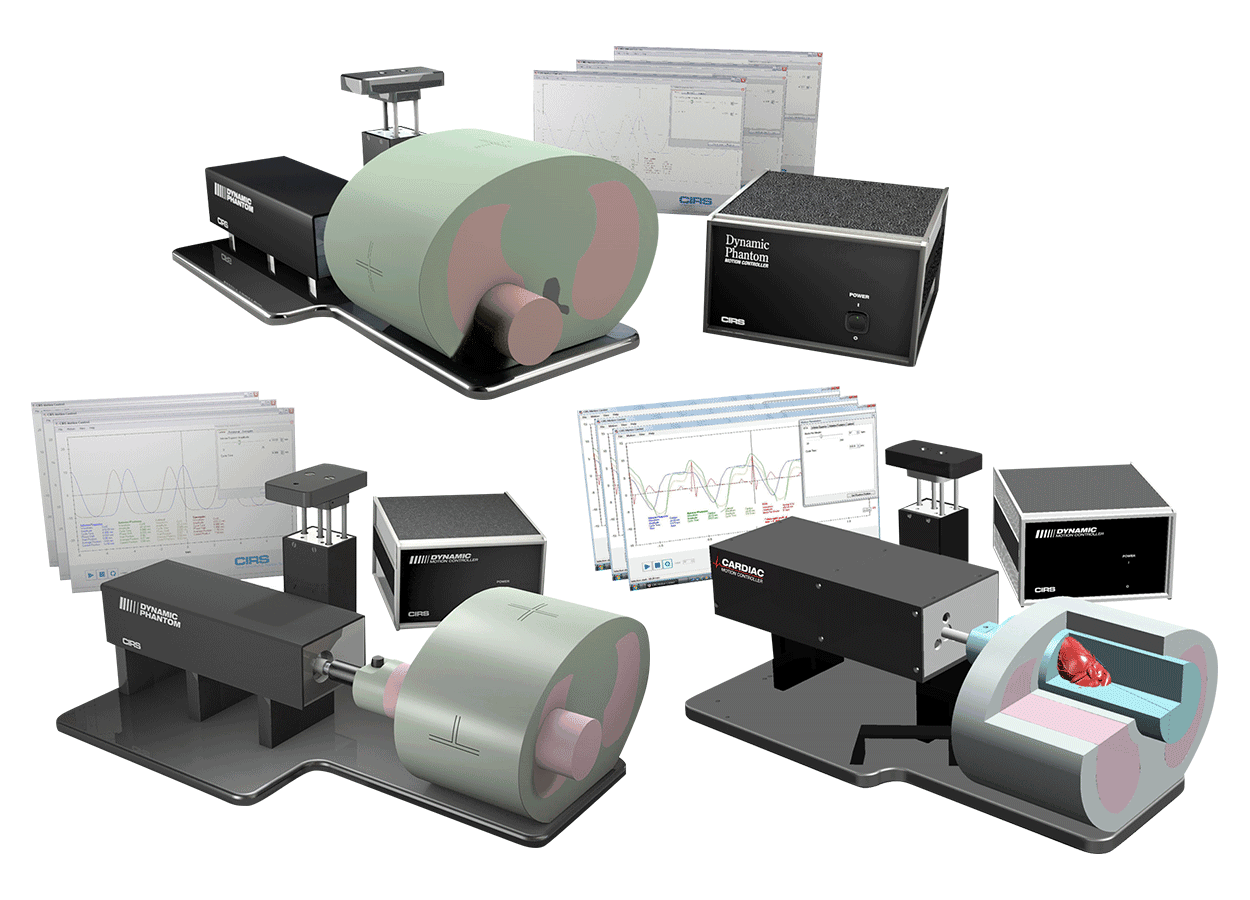
With tissue-equivalent construction and 3D motion, the Motion Management QA Phantoms comprehensively analyze image acquisition, planning, and dose delivery.
Tissue Equivalent Technology
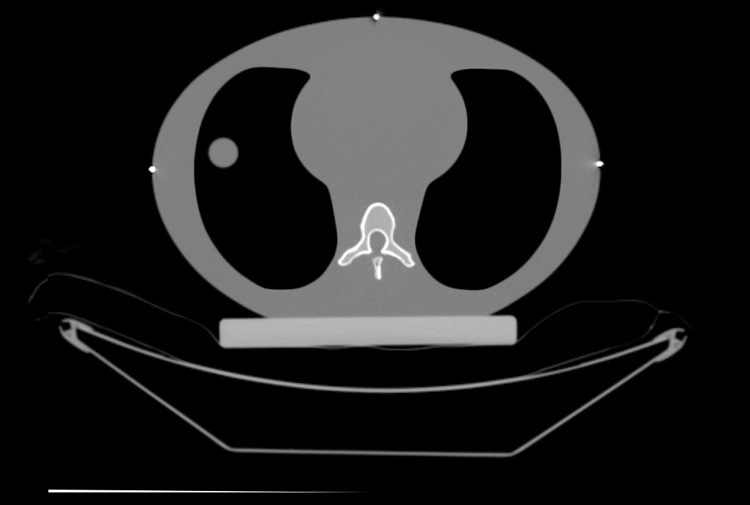
Linear attenuations of the simulated tissues are within 1% of actual attenuation for water and bone, and within 3% for lung from 50 keV to 15 MeV.
Motion Control Software
The Motion Management QA Phantoms are operated with user-friendly Motion Control software, which can be installed on any computer running Windows.
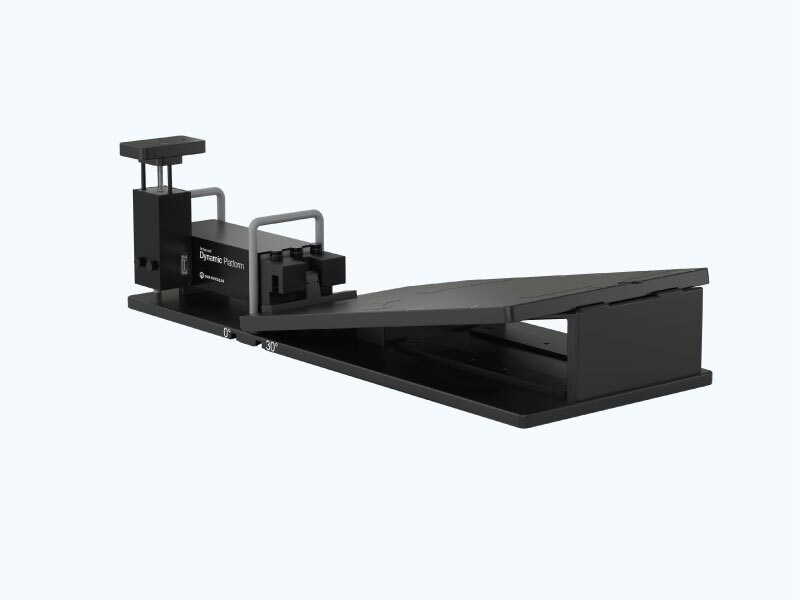
Independently Controlled Surrogate Motion
The surrogate motion, which is independent of the tumor motion, is programmable through the Motion Control Software.
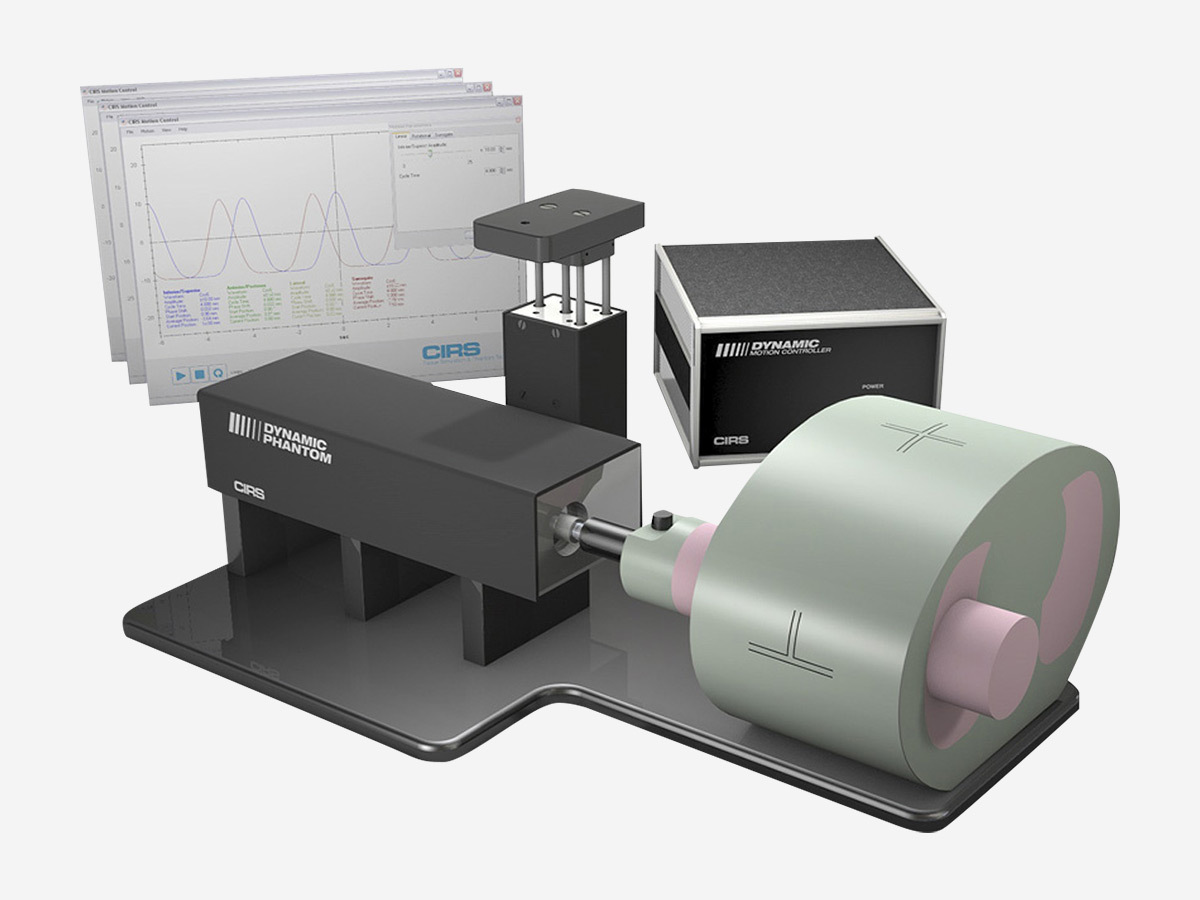
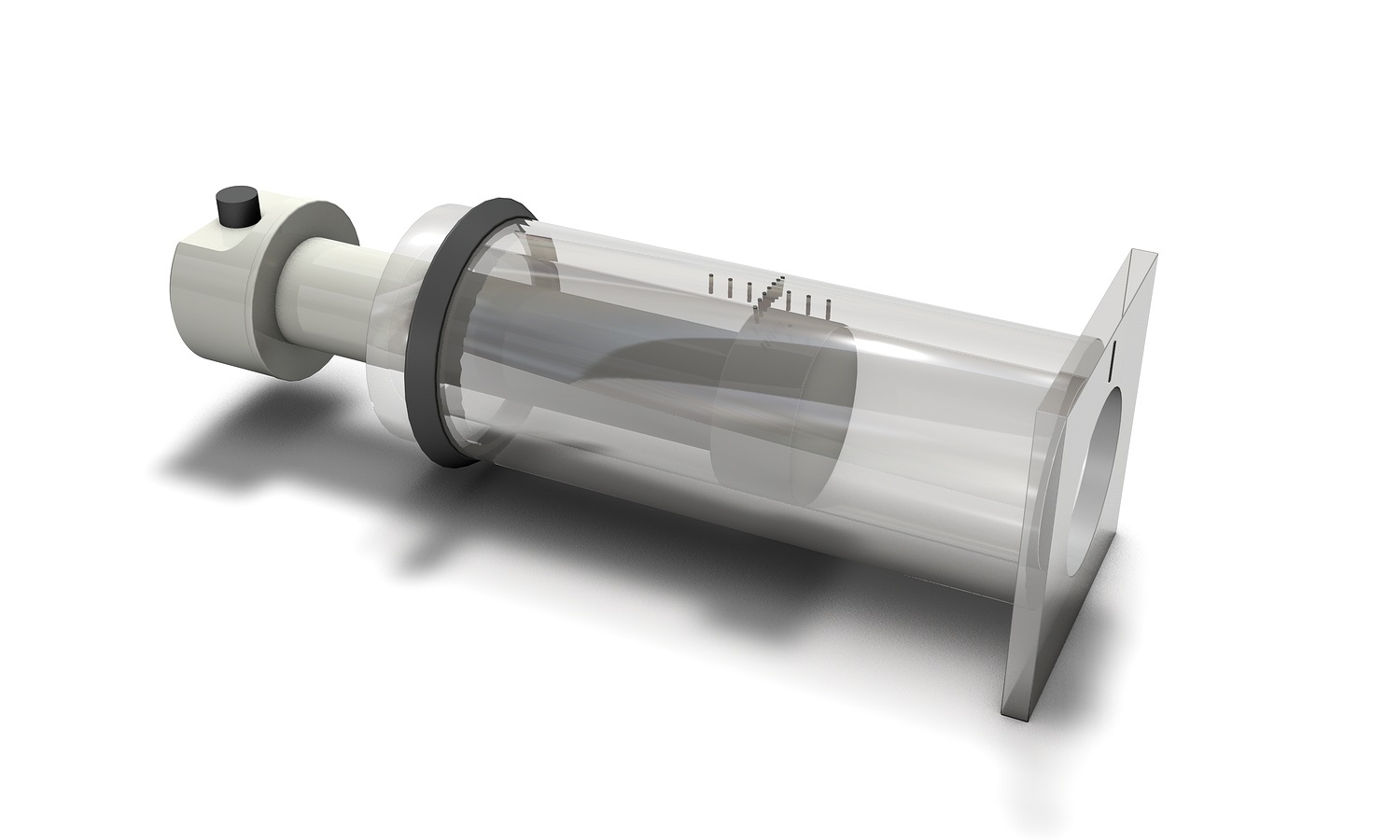
Dynamic Thorax Phantom
- Implement 4D imaging and radiotherapy systems
-
Quantify volumetric and positional aliasing of CT with a 3D target motion
-
Test accuracy and consistency of tumor tracking and respiratory gating devices
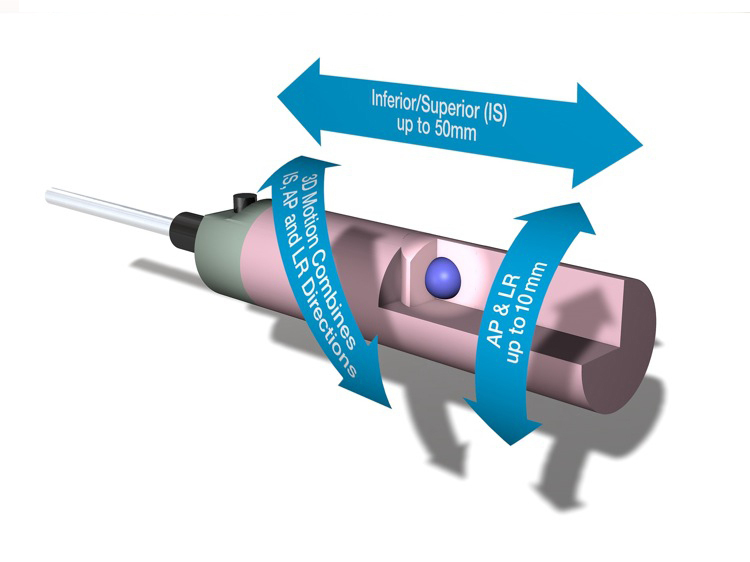
Complex 3D tumor motion within the lung
Compatible with TLD, MOSFET, micro-chamber, OSL, PET/ CT targets and film
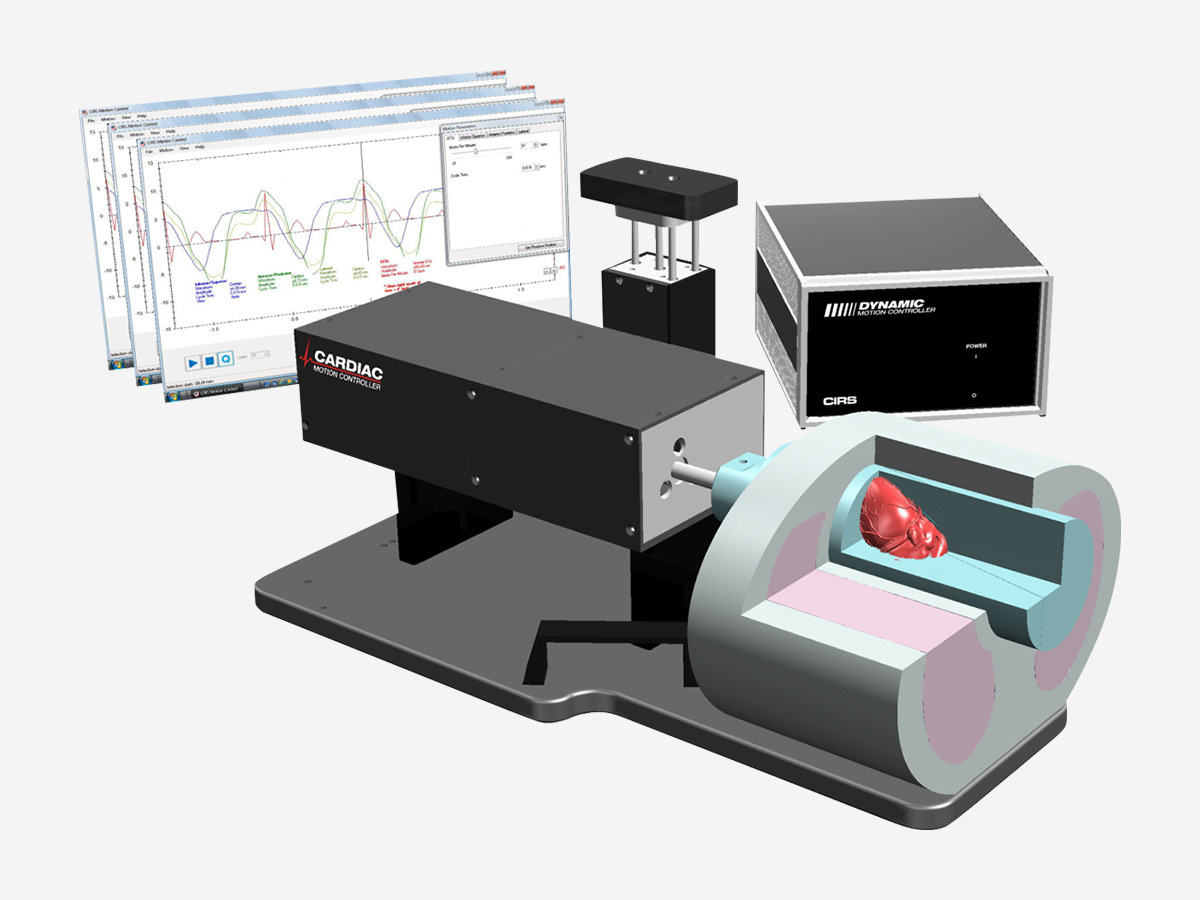
Dynamic Cardiac Phantom:
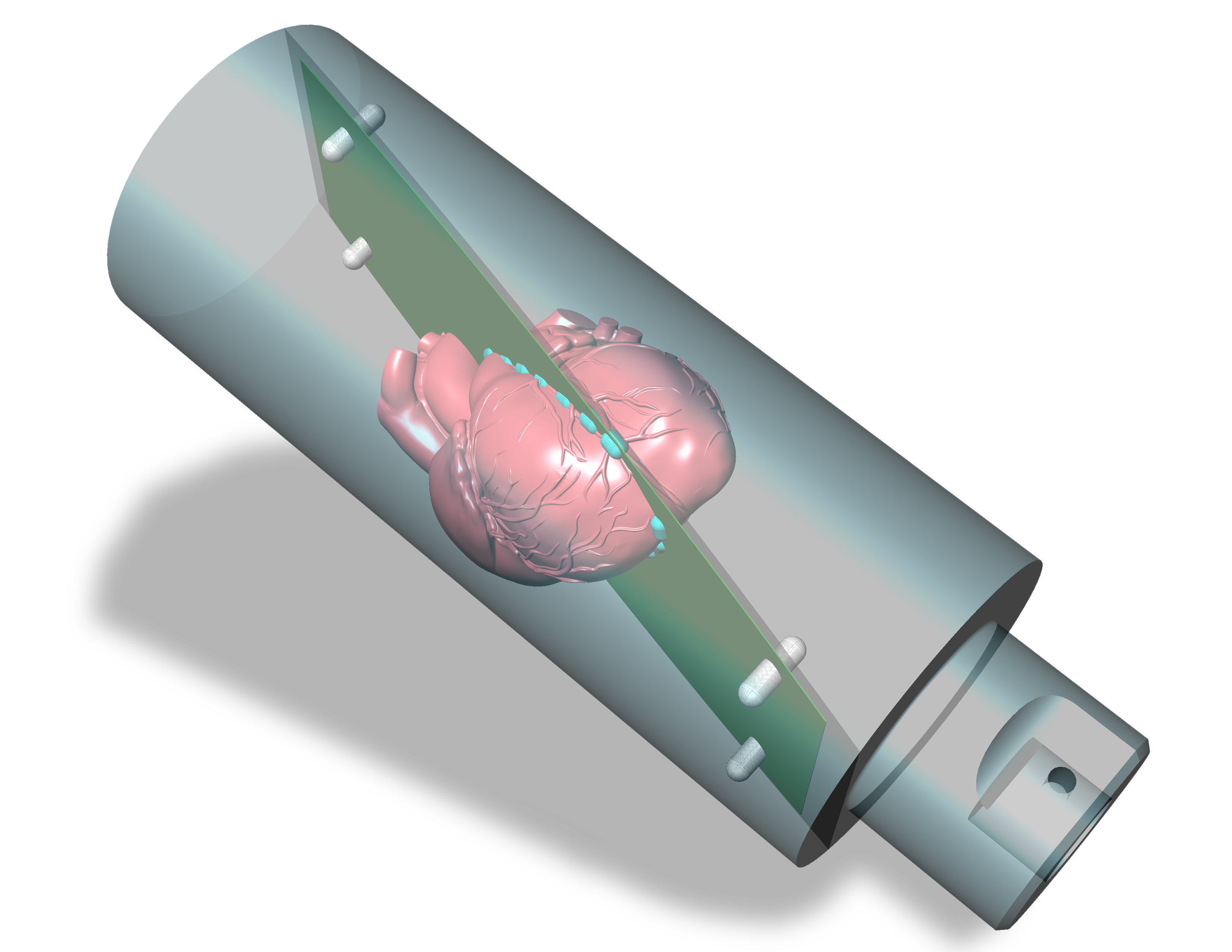
- Anthropomorphic heart inside a thorax body
- Iodine contrast and calcification detection capabilities
- Contrast target interchangeability
- Complex heart motion combined with respiratory motion
- Correlated ECG signal with readable output
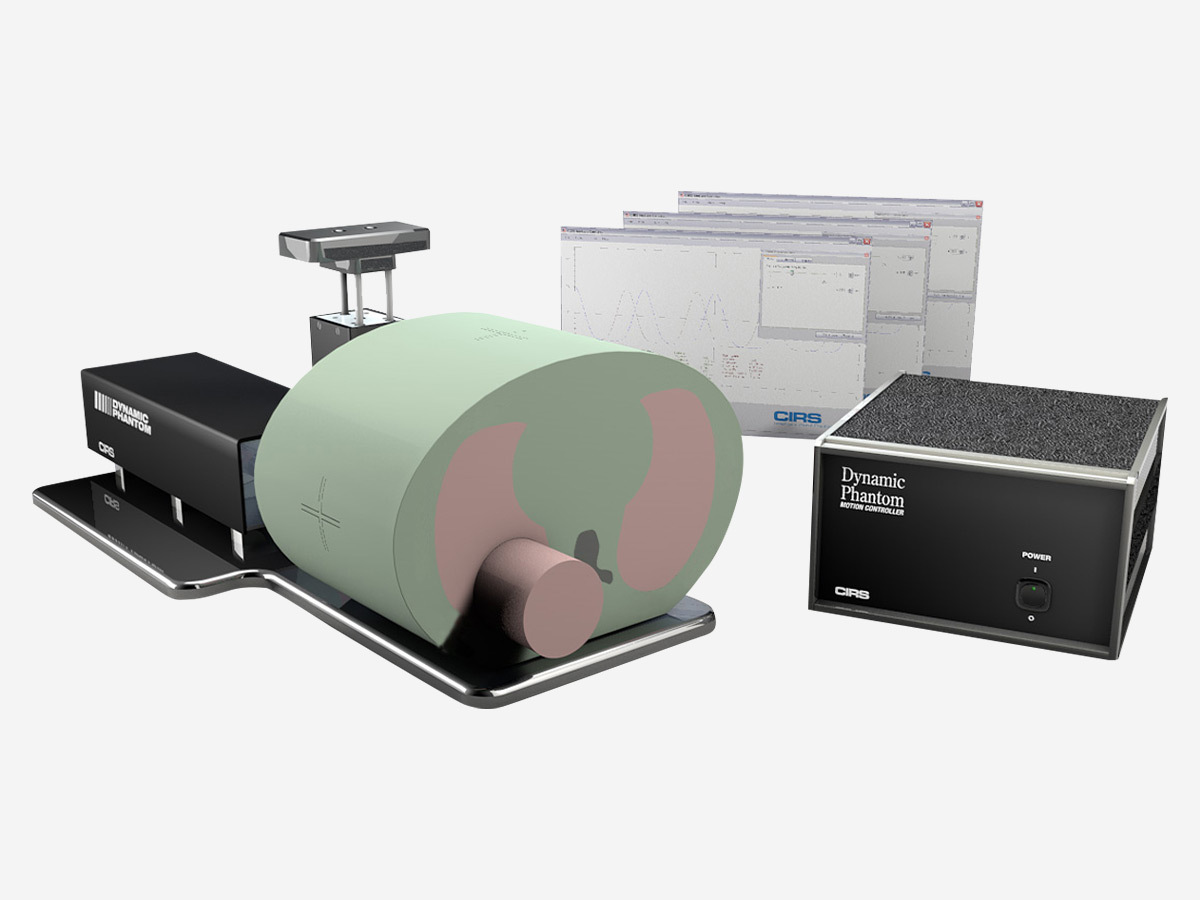
Xsight Phantom
- Verified and validated by Accuray for use with CyberKnife systems
- Use Xsight ® Spine Tracking System for initial phantom alignment
- Display detected respiratory motion of tissue-simulated torso, lung tumor, and critical structures with Synchrony System
- Execute E2E software analysis of the films (without CT number adjustment)
- Visualize 4D treatment optimization using the MultiPlan System
- 3D anthropomorphic spine with cortical and trabecular bone, ribs, and lung lobes
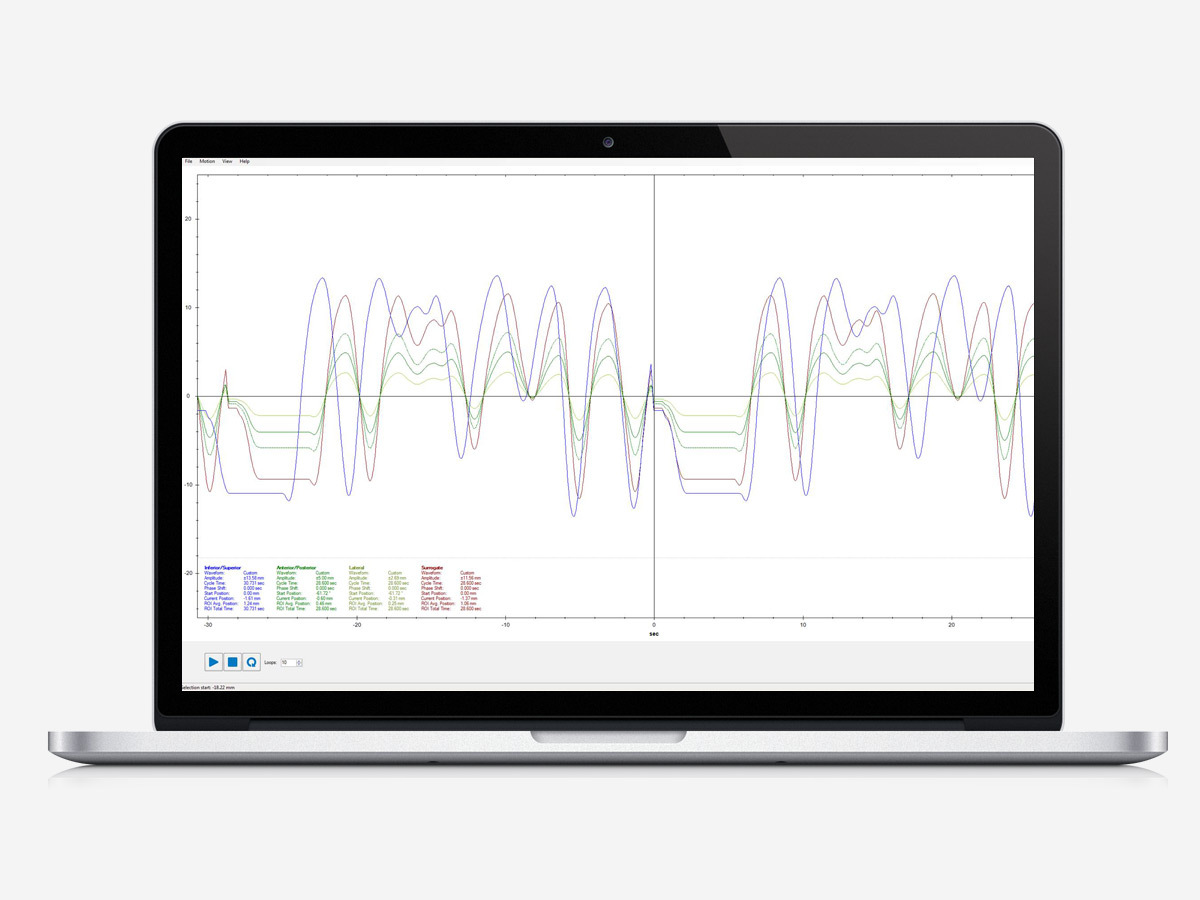
Motion Control Software
- Built-in and customizable waveforms
- Five built-in waveforms are available from a standard pull-down menu, and an unlimited number of clinically relevant and patient-specific waveforms can be imported
- Unlimited motion cycles
- Choose the number of cycles to be looped by entering the desired value or choosing continuous looping
- Advanced motion parameters
- The software automatically calculates the best scenario to simulate the real 3D waveform to achieve the simulated volume.
Looking for a better way to QA your motion management?
Resources
Specifications
Dimensions |
67 cm x 32 cm x 28 cm (26” x 15” x 11”) |
Weight |
17.2 kg (37.9 lb) |
Power |
110-250 VAC, 50/60 Hz |
Amplitude, IS |
± 25 mm |
Amplitude, AP/LR |
± 5 mm |
Amplitude, Surrogate |
± 25 mm |
Max. Surrogate Platform Load |
5.4 kg (12 lb) |
Motion Accuracy |
± 0.1 mm |
Cycle Time |
1 - ∞ (adjusted based on amplitude) |
Waveforms |
sin (t), 1-2cos4(t), 1-2cos6(t), sawtooth, sharkfin |
Motion Control Software System Requirements |
Windows XP® or later (32 or 64 bit) Pentium 3® or equivalent 512 MB RAM 2 MB of available disk space |
| MoreLess | |
Dimensions |
71 cm x 32 cm x 28 cm (28” x 13” x 11”) |
Weight |
18.6 kg (41 lb) |
Power |
110-250 VAC, 50/60 Hz |
Amplitude, IS |
± 5 mm Heart Beating; ± 25 mm Breathing |
Amplitude, AP/LR |
± 8 mm AP; ± 6 mm LR |
Amplitude, Surrogate |
± 25 mm |
Max. Surrogate Platform Load |
5.4 kg (12 lb) |
Motion Accuracy |
± 0.2 mm |
Cycle Time |
1 - ∞ (adjusted based on amplitude) |
Waveforms |
sin (t), 1-2cos^4(t), 1-2cos^6(t), sawtooth, sharkfin, heart beat, heart beat + breathing |
| MoreLess | |
Power |
110-250 VAC, 50/60 Hz |
Amplitude, IS |
± 25 mm |
Amplitude, AP/LR |
± 5 mm |
Amplitude, Surrogate |
± 25 mm |
Max. Surrogate Platform Load |
5.4 kg (12 lb) |
Motion Accuracy |
± 0.1 mm |
Cycle Time |
1 - ∞ (adjusted based on amplitude) |
Waveforms |
sin (t), 1-2cos4(t), 1-2cos6(t), sawtooth, sharkfin |
Motion Control Software System Requirements |
Windows XP® / Vista / Windows 7/ Windows 8/ Windows 10 (32 or 64 bit) Pentium 3® or equivalent 512 MB RAM 2 MB of available disk space |
| MoreLess | |